Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) have emerged as one of the most exciting inventions in the field of Artificial Intelligence (AI) since their conception by Ian Goodfellow and his colleagues in 2014. This machine learning paradigm focuses on an architecture consisting of two concurrent neural networks: a generator and a discriminator. The generator creates samples from random noise, while the discriminator evaluates these samples against real data, setting up a theoretical zero-sum game that reflects a form of minimax in game theory.
Foundations and Evolution
At the heart of GANs lies the minimization of the Jensen-Shannon divergence, a measure of similarity between two probability distributions. Mathematically, the generator (G) aims to minimize the value function (V(G, D)) while the discriminator (D) seeks to maximize it, where:
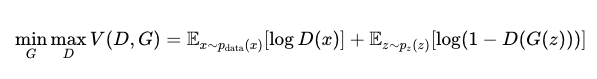
Initially, GANs faced significant challenges such as training instability and mode collapse, where the generator produces a limited variety of outputs. Over time, they have evolved through various advancements, with the Wasserstein GAN (WGAN) and Conditional GAN (CGAN) standing out. WGAN introduces the Wasserstein distance as an alternative to Jensen-Shannon minimization, mitigating the instability issue. Meanwhile, CGAN incorporates contextual information, allowing for the generation of data to be directed towards more specific domains.
Recent Advances and Innovative Techniques
A substantial improvement in image generation is demonstrated in BigGAN, which scales GANs by leveraging large datasets and deep network architectures. Another model breakthrough is StyleGAN, which has gained notoriety for its ability to synthesize hyperrealistic human faces. StyleGAN introduces a variation of the latent space that enables specific manipulations of features, leading to unprecedented personalization in image generation.
Diving deeper into the robustness of GANs, GAN Geometry explores the structure of the latent space, revealing how specific variations in this space correlate with discernible semantic changes in data generation. This knowledge proves vital for applications such as AI-assisted design and the generation of adaptable content.
Practical Applications at the Forefront
In practice, GANs have started a revolution in areas such as drug synthesis, where they accelerate the discovery of viable chemical compounds, and in medical imaging enhancement, facilitating the acquisition of high-resolution images from lower-quality samples. The potential also extends to digital art, where artists and systems collaborate to produce works that challenge traditional authorship and creativity.
Illustrative Case Studies
- DeepMind has used GANs to generate intricate protein maps with a degree of fidelity that challenges traditional bioinformatic techniques.
- In the entertainment domain, NVIDIA utilizes StyleGAN to create user avatars on gaming platforms and virtual reality applications, offering deeply immersive personalization.
Current Challenges and Projections
Despite their undeniable power, GANs face ethical and legal issues, especially concerning the creation of “deepfakes” and their potential for malicious use. Questions arise regarding the consent and privacy of synthesized data that mirrors real individuals.
Technically, the evaluation of GANs remains challenging, with the Inception Score (IS) and the Frechet Inception Distance (FID) being two relevant, albeit imperfect, metrics that aim to quantify the quality and diversity of the generated images.
The future promises multimodal GANs capable of understanding and synthesizing cross-data among text, image, and sound, paving the way for revolutionary media synthesis systems. Additionally, advances in the automatic interpretation of natural language with applications in voice synthesis and translation are imminent.
Conclusion
GANs serve as a prism through which we glimpse the future of AI: an intersection of creativity and autonomy. The continuous refinement of these adversarial systems promises to not only enhance existing applications but also to unlock domains of artificial intelligence that have yet to be explored. Embracing both technical advances and ethical challenges, GANs define a horizon of innovation and responsibility in the era of ubiquitous AI.






















